AltAI neuromorphic chip
The AltAI neuromorphic chip is a joint project by Motiv-Neuromorphic Technologies and Kaspersky.
First-generation AltAI neuromorphic
chip (AltAI-1)
AltAI-1 is a very-large-scale integration (VLSI) circuit designed to run (inference) spiking neural networks efficiently. The AltAI-1 architecture uses a near-memory computing approach to avoid the excessive energy consumption typical of von Neumann architectures during data transfers between the memory and the computing core. As a result, the AltAI-1 neuromorphic chip consumes less power.
The main structural unit of the AltAI-1 architecture is a core. A core combines a group of neurons and the memory to store their parameters. Within the core, the function of neurons is performed by a finite state machine that models their behavior.
The operation of all neurons in an SNN is synchronized with a tick signal. When this signal is given, the potentials of all neurons are sequentially updated by all cores, and spikes are emitted as needed. A core performs, among other things, 262 144 synaptic operations per tick. At the same time, the tick frequency can reach 2000 Hz. One synaptic operation is performed in one clock cycle at a frequency of up to 600 MHz.
AltAI-1 has a regular core structure arranged in a rectangular grid, where each core is directly connected to its four neighbors (see Fig. 1).
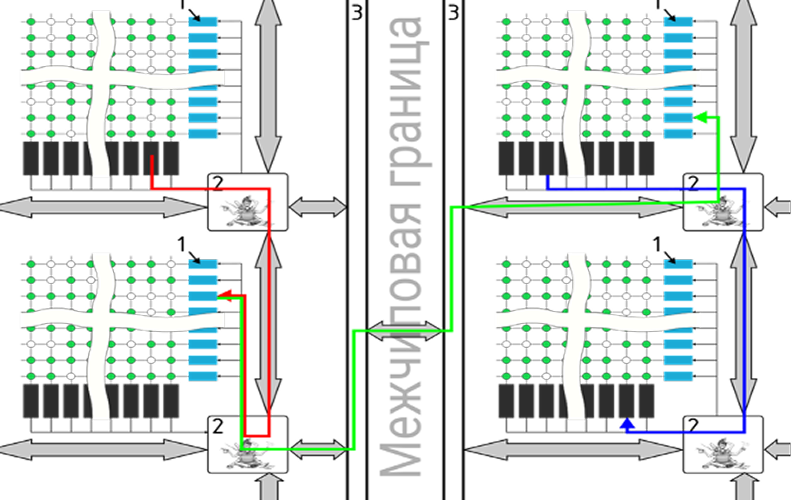
Fig. 1 - AltAI-1 core network Legend: 1: core input line, 2: router, 3: packet multiplexer
A specially designed signal routing mechanism is used for transmitting spikes between neurons belonging to different cores. Accordingly, when a neuron function is performed, the potentials sent by neurons from other cores can be added to the potential of the neuron being modeled.
Currently, AltAI-1 prototypes have been released featuring 16 neurocores with 512 neurons per core, offering the capability for inferencing SNNs.
Boards with 8 and 16 AltAI-1 prototypes have been manufactured. The board with 8 chips is a neuromorphic computing accelerator that connects to a backplane in a desktop form factor (see Fig. 2). Up to 16 accelerators can be connected to one backplane.
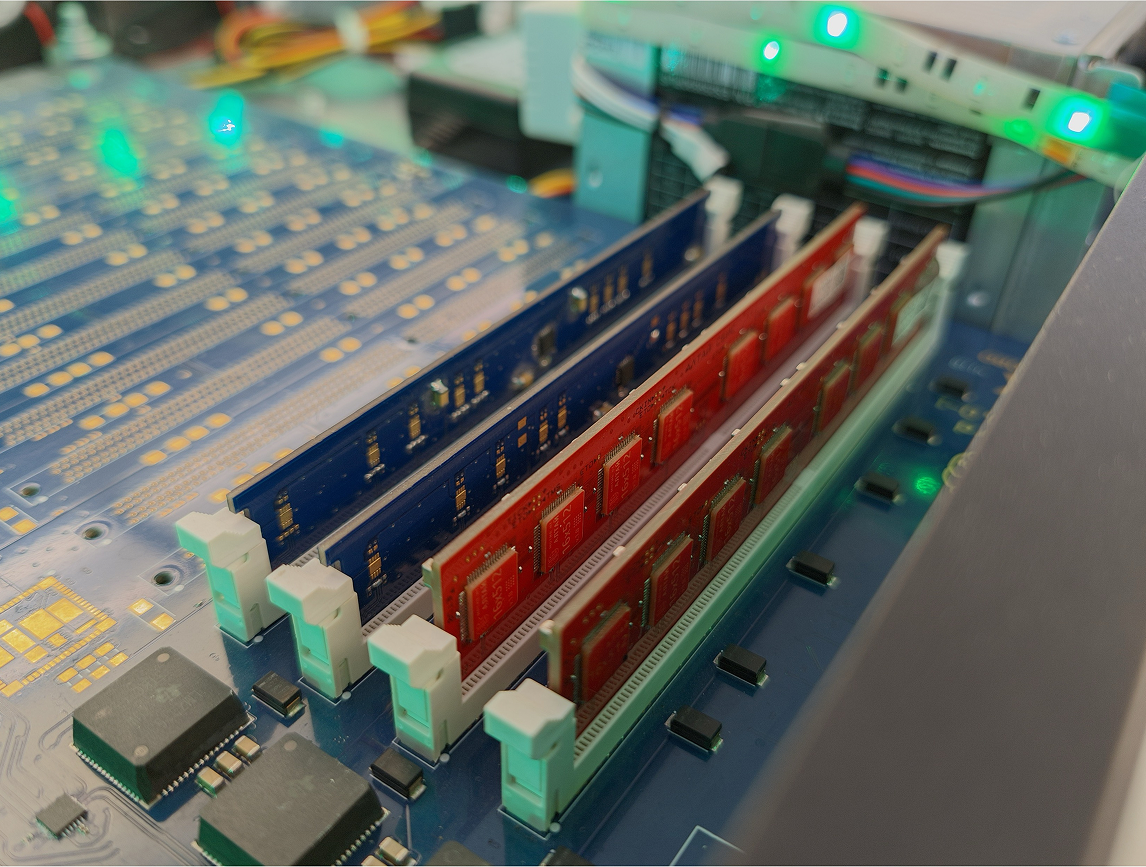
Fig. 2 – Backplane with AltAI-1 neuromorphic computing accelerators
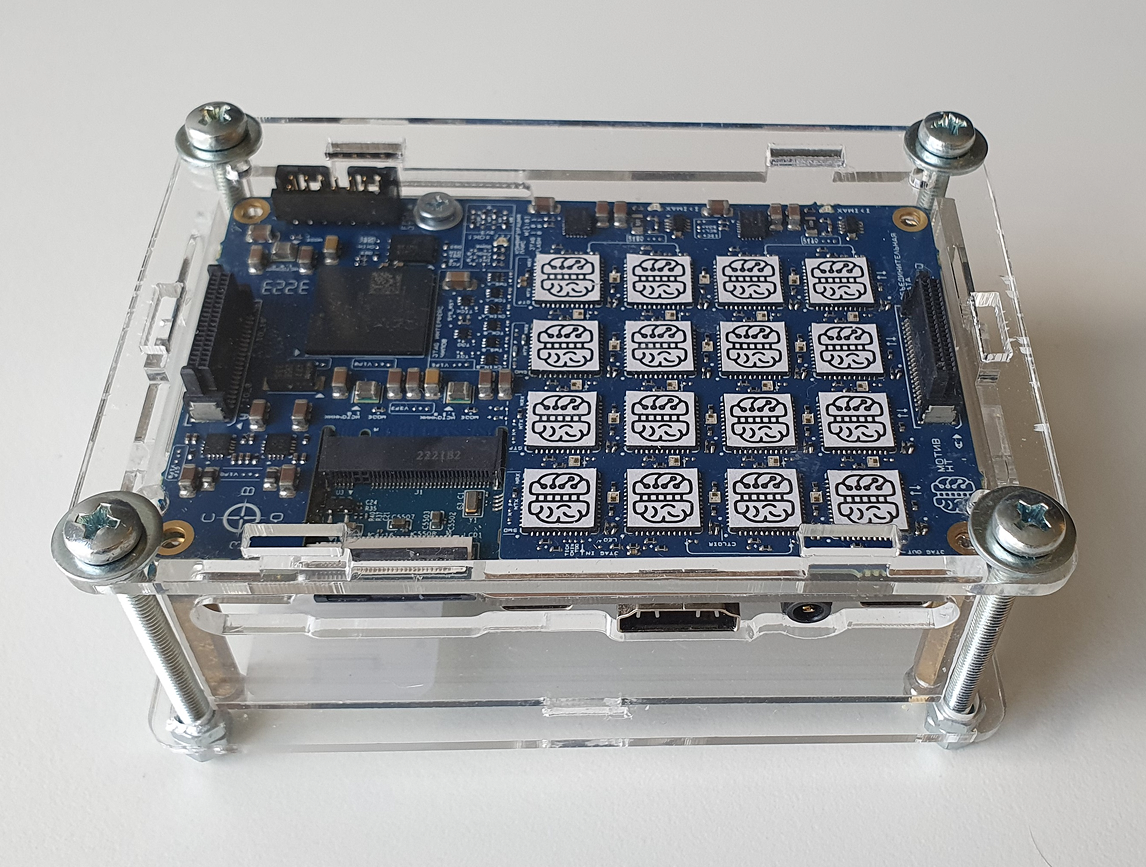
Fig. 3.1 – Backplane with 16 AltAI-1 chips
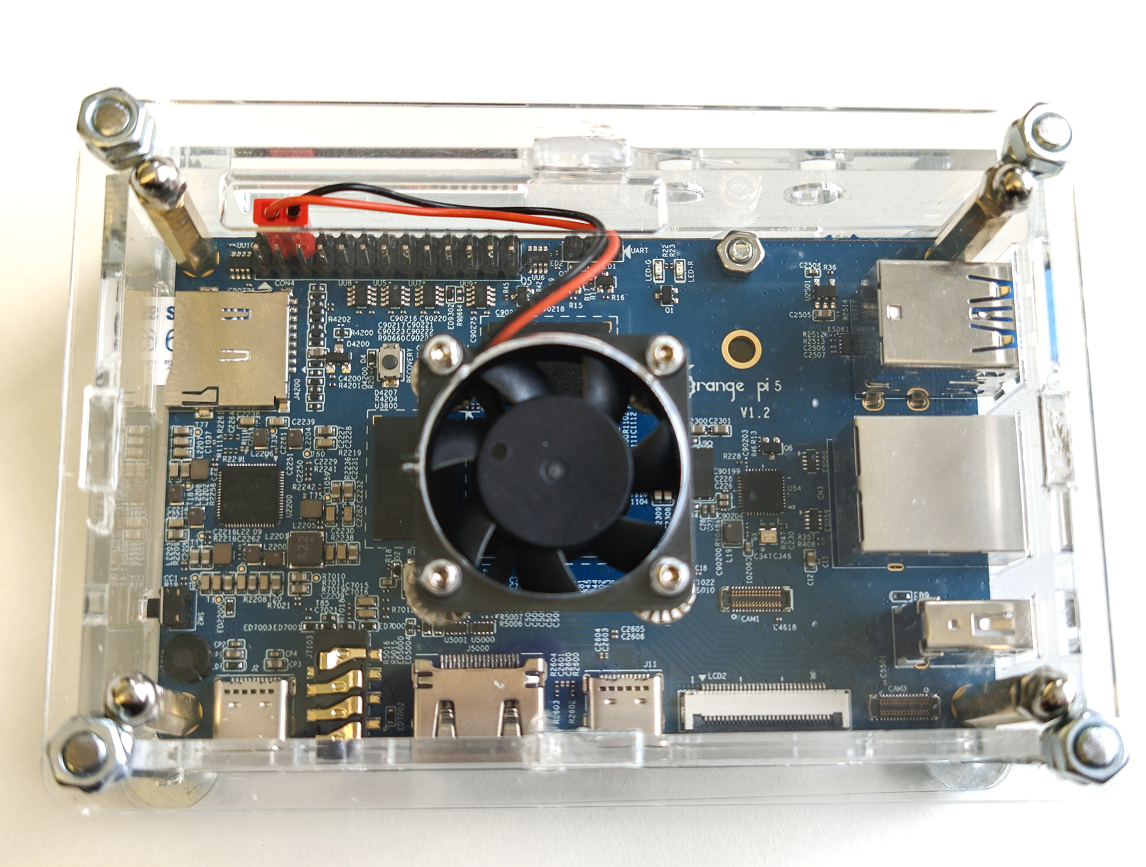

Fig. 3.2 – Сonnected to an OrangePi5 board (right) via PCI-E
The board with 16 chips is designed in an embedded system form factor and is structurally compatible with edge boards like OrangePi5 via the PCI-E interface (see Fig. 3.1, Fig. 3.2).
Kaspersky Neuromorphic Platform (KNP) supports the AltAI-1 as a hardware backend.
See the Research section for multiply proofs of concept using the AltAI-1 prototype and KNP.
Second-generation AltAI neuromorphic
chip (AltAI-2)
The release of the second-generation AltAI chip (AltAI-2) is planned for 2026. AltAI-2 will have a number of important new features:
- Online learning;
- Programmable neuron model;
- Programmable synaptic function;
- Dynamic neural network structure.
This marks another step towards creating neuromorphic AI systems that are not only energy-efficient and fast but also adaptive.
All AltAI-2’s new features will also be supported in the Kaspersky Neuromorphic Platform. This will allow the specific hardware architecture of AltAI-2 to be taken into account during SNN development, ultimately leading to the creation of computationally efficient edge solutions on this hardware platform.
Contact
To discuss collaboration opportunities, please email us at neuro@kaspersky.com,
or use the contact form below




